Fair value, in the investing world, is the value an individual investor assigns to a company’s marketable securities based on his or her analysis of a company’s financial information. Fair Value is the one of the most important parameter in Fundamental Analysis of the Stock. It provides valuation of an asset on an ongoing basis to the investor based upon the company’s reported financial information.
It is considered fair value as it is driven based upon financial data and the price agreed upon by both sides, the seller and the buyer, to benefit from the transaction at the particular price.
For example, Company A sells its stocks to company B at Rs. 80 per share. Company B thinks he could sell it at Rs. 100 per share once it acquires the same and so decides to buy a million shares at the original price. It is considered fair value because the price was agreed by both sides and they both benefit from the sale.
Market value is different from Fair Value.
Some people use fair value and market value as a same thing but there is difference between these two terms. Fair value is the price at which asset is exchange between knowledgeable parties at arm’s length transaction. Market value is price at which the asset is exchanged between parties in the market.
Market Value of the stock moves around Fair Value of its own most of the time and it keeps on changing as and when there is change in fundamentals of the Company. If, the market price of any stock is less than its fair value then the stock is called undervalued with respect to the Fair Value. In such a scenario there is higher probability of market price of the stock moving upwards. If the market price is more than its Fair Value then the stock may be overvalued with respect to the Fair Value. And market price of the stock may decrease.
For Example:
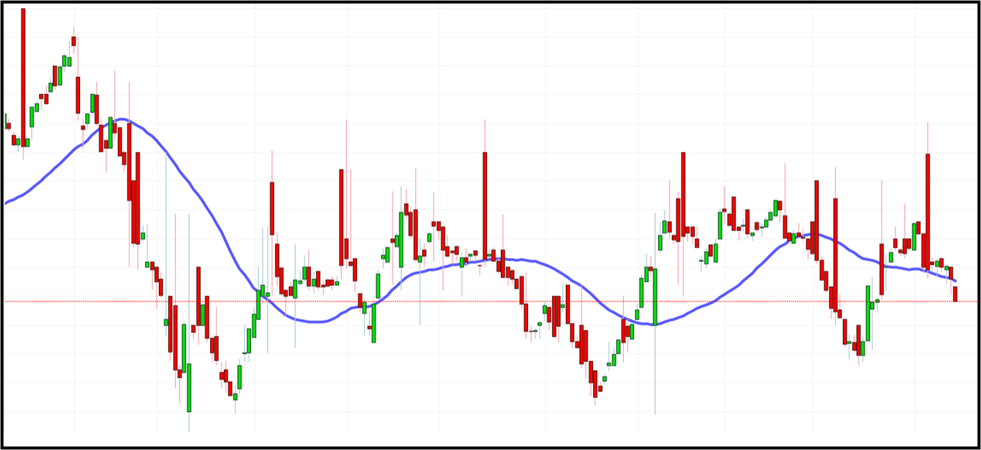
Let’s consider the following chart of a particular stock where candlesticks represent the Stock Market Price where as Blue line is showing Fair Value of the stock over a period of time. It can be easily observes that whenever Price (Candlesticks) goes far away from the Fair Value line, they been pulled towards the line. This phenomenon can be seen as similar to mean reversion.